Conditions
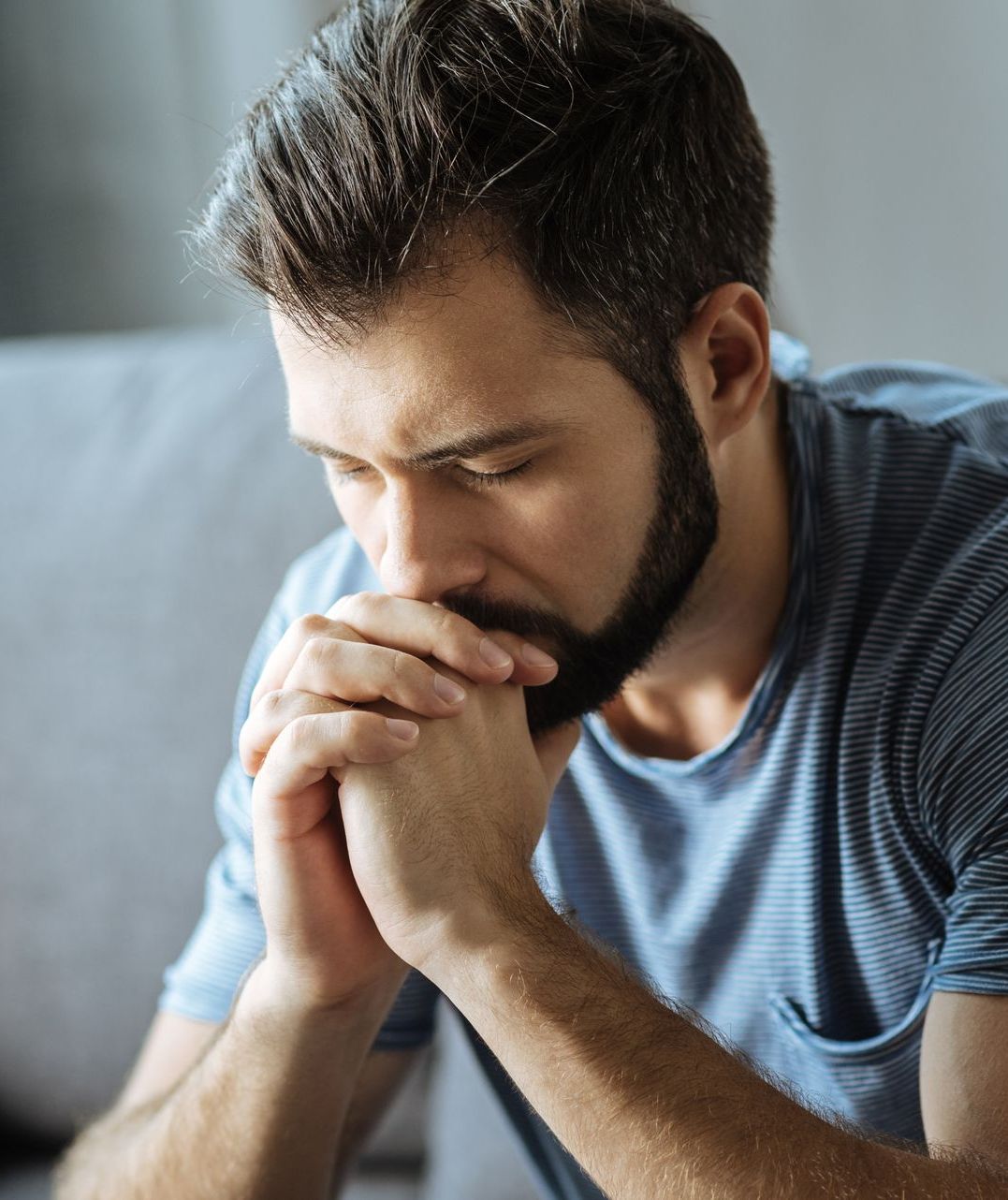

Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism is a condition where the body doesn't produce enough sex hormones, affecting sexual development and function. It can be due to gonadal issues (primary hypogonadism) or brain regulation problems (secondary hypogonadism). Symptoms vary by age and sex; men may see reduced hair growth, muscle mass, and erectile function, while women might face menstrual and fertility issues. It can also weaken bones and impact mood and libido. Treatment often involves hormone replacement therapy, customized to the individual's needs. Early detection and treatment are crucial to reduce long-term effects.
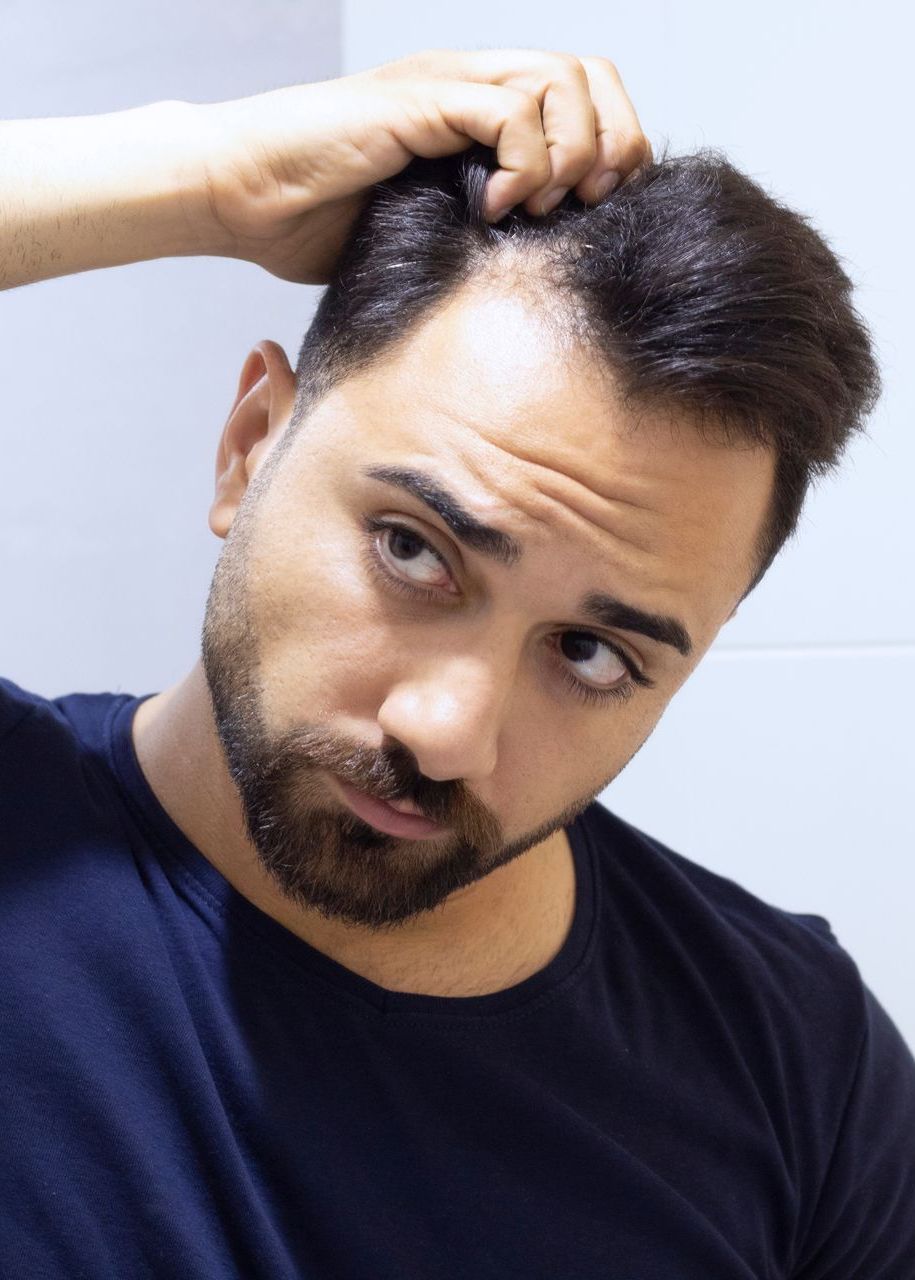

Hair Loss (Men)
Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia): Also known as male pattern baldness, this is the most common cause, characterized by a receding hairline and balding on the crown.
Hormonal Changes: Changes in androgen levels can lead to hair loss.
Medical Conditions: Such as thyroid disorders, scalp infections like ringworm, and autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata.
Medications: Drugs used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, gout, and high blood pressure can cause hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients like iron, protein, and vitamins can contribute to hair thinning.
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger temporary hair loss.
Harsh Hair Treatments: Overstyling, strong chemicals, and heat treatments can damage hair.
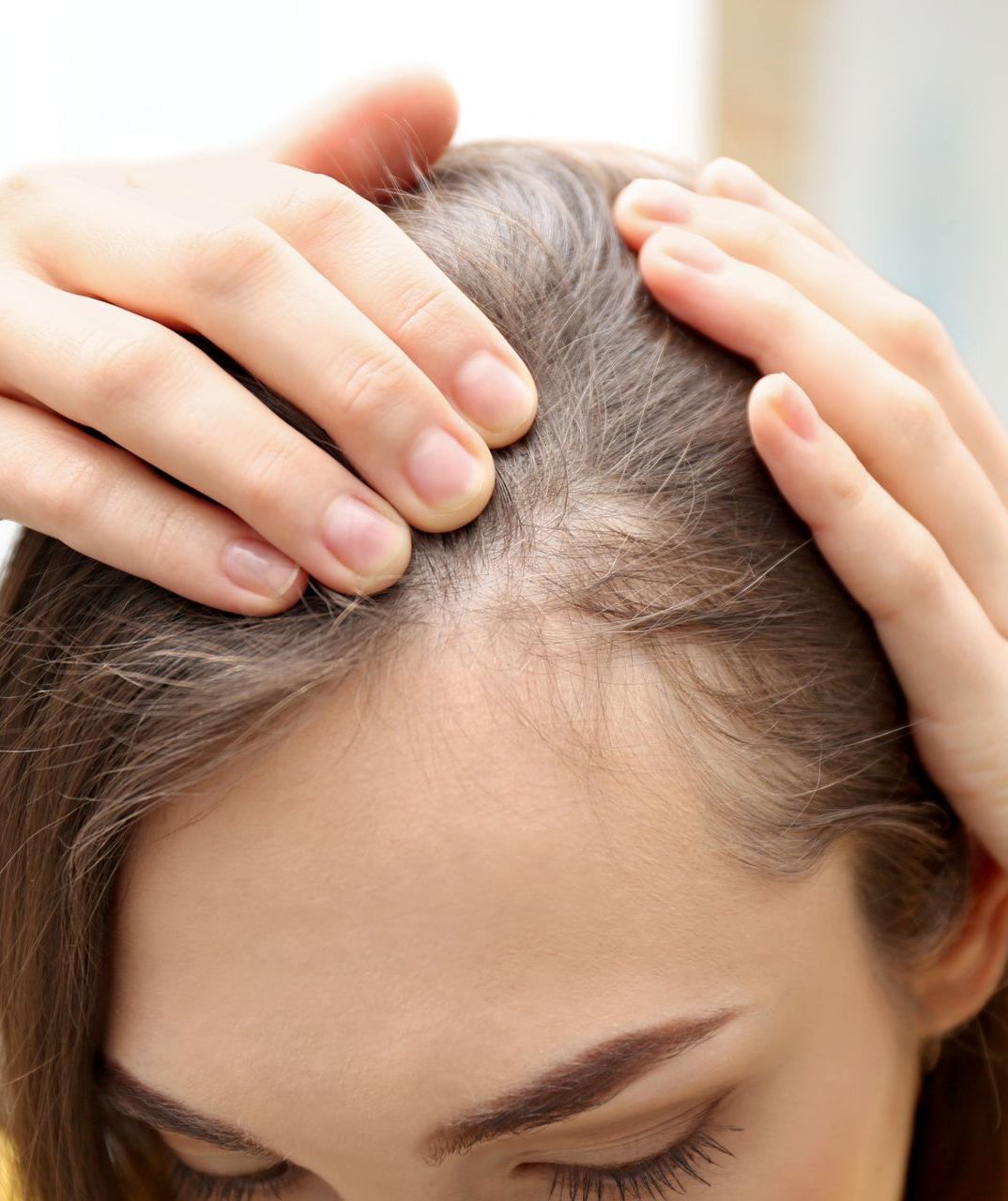

Hair Loss (Women)
Genetics (Female Pattern Hair Loss): Women may experience overall thinning without a receding hairline.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid problems can cause hair loss.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can lead to hair thinning.
Medications: Similar to men, certain medications can cause hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Particularly lack of iron, protein, and other essential nutrients.
Stress: Severe stress can lead to temporary hair shedding.
Hairstyles and Treatments: Tight hairstyles and harsh chemical treatments can cause hair loss.
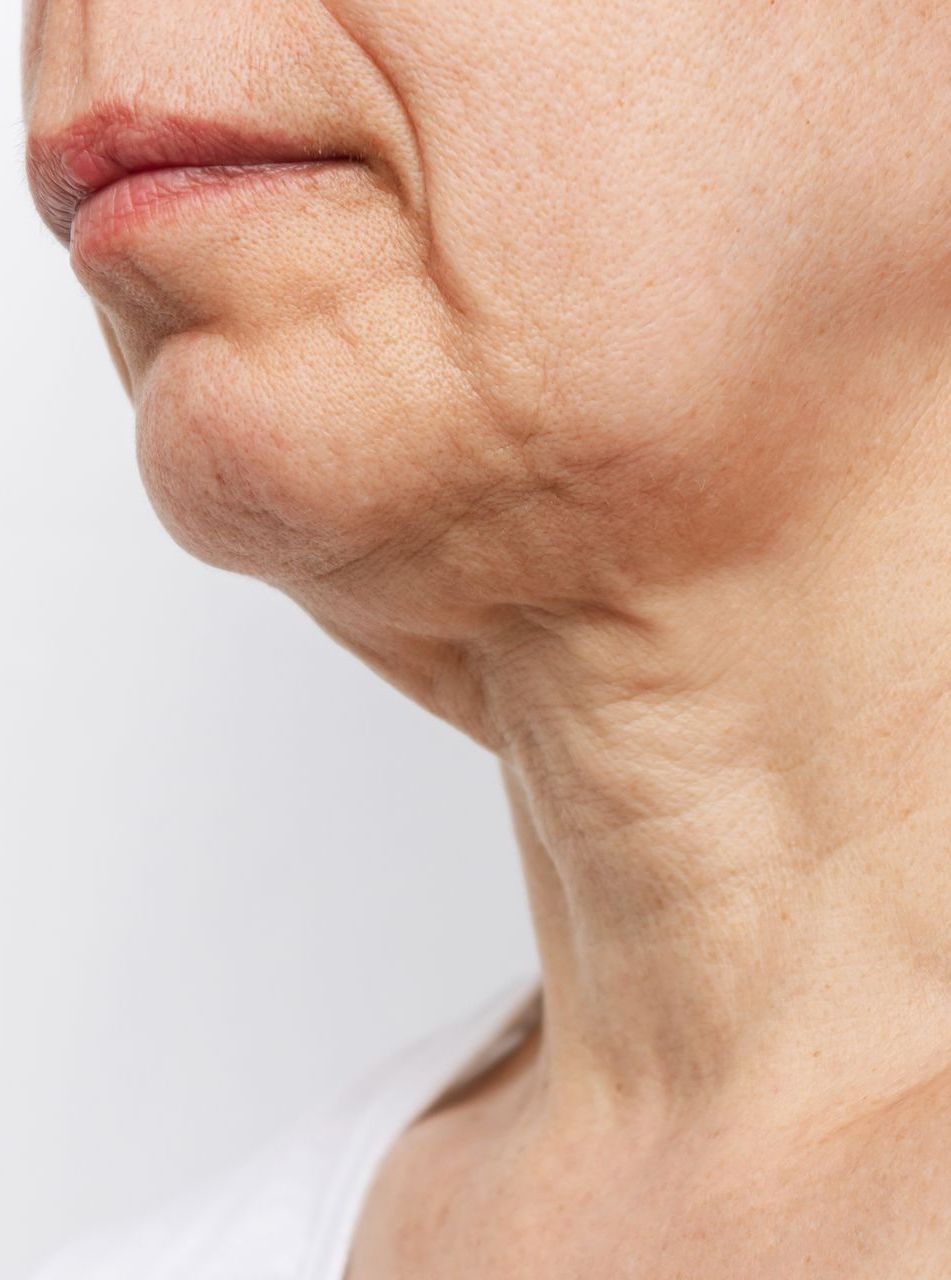
Sagging Skin (Face)
Sagging facial skin, commonly linked with aging, occurs due to reduced collagen and elastin production, leading to less firm and elastic skin. Contributing factors include sun exposure, significant weight loss, and unhealthy lifestyle habits like smoking, along with genetic influences. While it affects more than just appearance, potentially impacting self-esteem, various treatments exist, from collagen-boosting creams to facelifts and laser therapy. Prevention, including sun protection and hydration, is crucial in managing this condition.
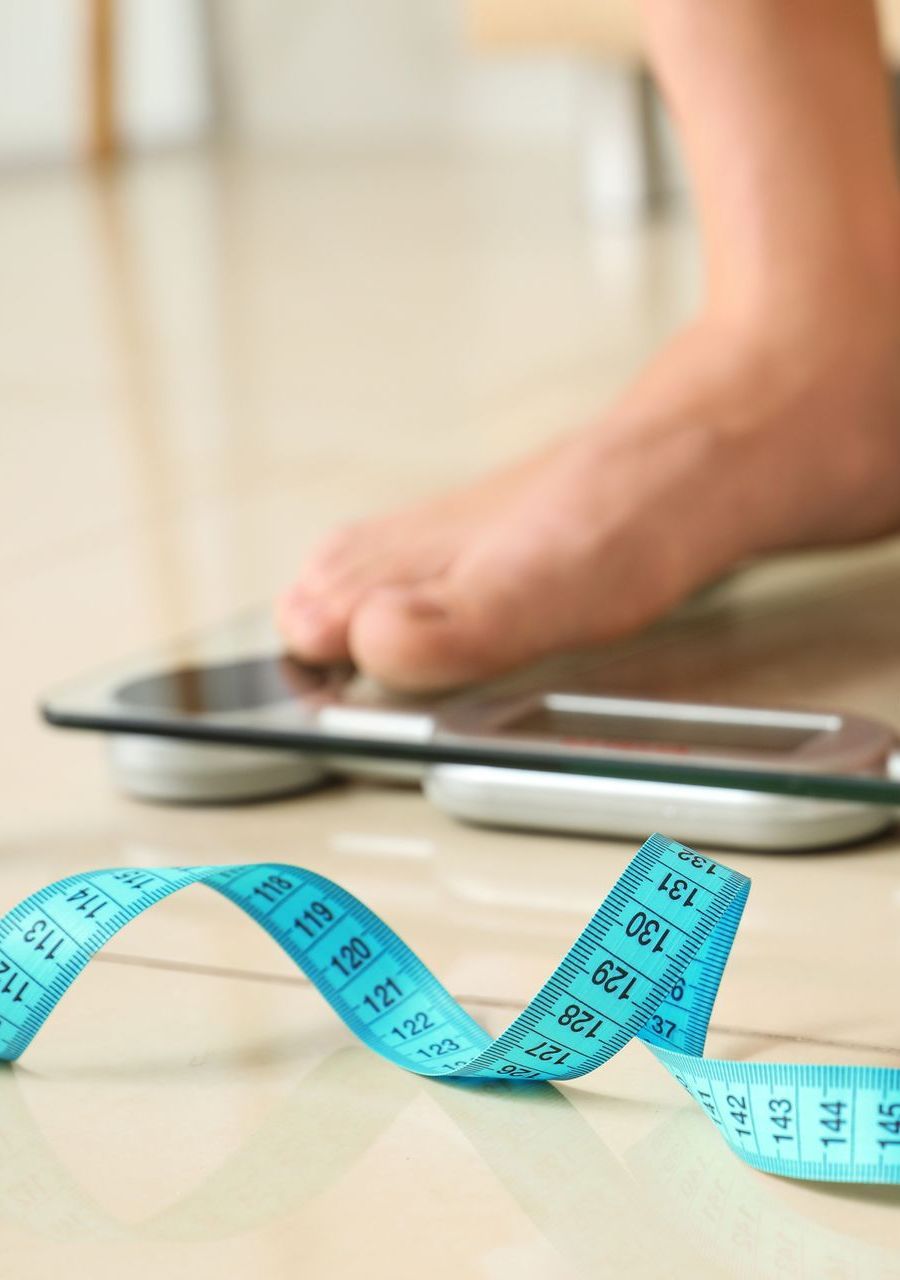

Obesity
Obesity is a complex health condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, which poses significant risks to overall health. It's often the result of a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, including high calorie intake, sedentary lifestyle, and metabolic influences. Obesity substantially increases the risk of numerous diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain cancers. Its management typically involves lifestyle changes like a healthier diet and increased physical activity, and in some cases, medical interventions like medication or surgery. Addressing obesity is crucial not only for individual health but also for reducing the societal burden of related health complications.
OFFICE HOURS
Monday - Saturday: 9 AM - 5 PM
Sunday: Closed